Building instrumentation and control technologies into the design of the next generation of advanced nuclear reactors will help the industry meet zero-carbon-emissions goals.
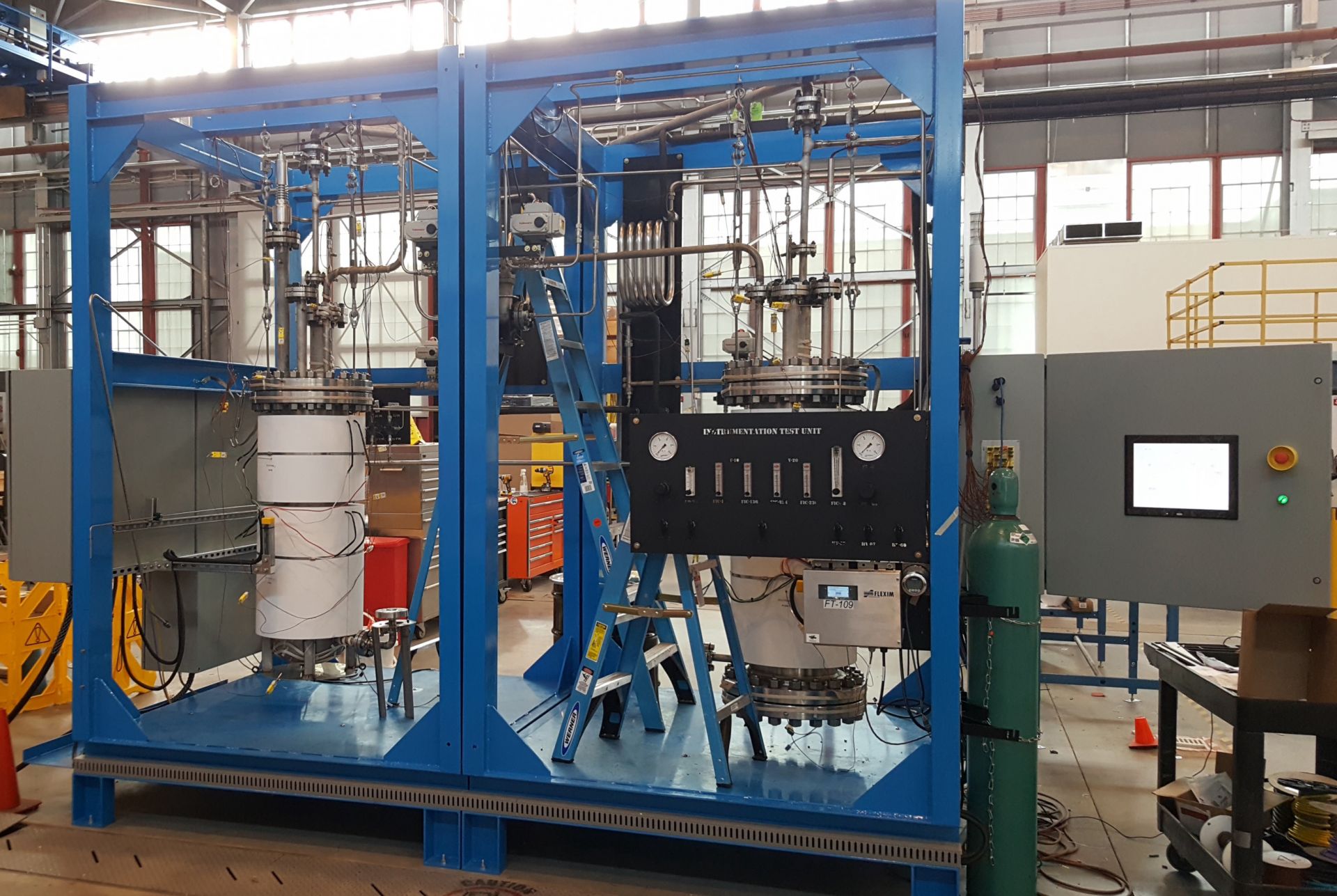
December 23, 2021, 3:00PMNuclear NewsAlexander Heifetz, Matthew Weathered, Nathan Hoyt, Mark Anderson, Scott Sanders, Anthonie Cilliers Kairos Power’s Instrumentation Test Unit
As a source of carbon-free electricity, nuclear energy currently dominates in the United States. However, the light water reactors in the U.S. are approaching the end of their licensed service lives. Meanwhile, low-cost electricity generated by fossil fuel–based sources (such as natural gas) poses an ongoing challenge to the economic viability of commercial nuclear reactors. To enhance the competitiveness of the nuclear industry, we need to bring down the high operating and maintenance (O&M) costs through savings available from utilizing modern, efficient sensing and automation technologies.
The Summit supercomputer at Oak Ridge National Laboratory began operations in 2018. (Photo: ORNL)
The Department of Energy has announced $9.25 million for research into the behavior and properties of structural materials under molten salt reactor conditions through collaborations using the DOE’s high-performance supercomputers.
The Molten Chloride Reactor Experiment will be built at Idaho National Laboratory to demonstrate criticality in a fast-spectrum salt-cooled reactor within five years. (Image: Southern Company)
Artist’s conception of Oklo’s Aurora powerhouse. (Image: Gensler)
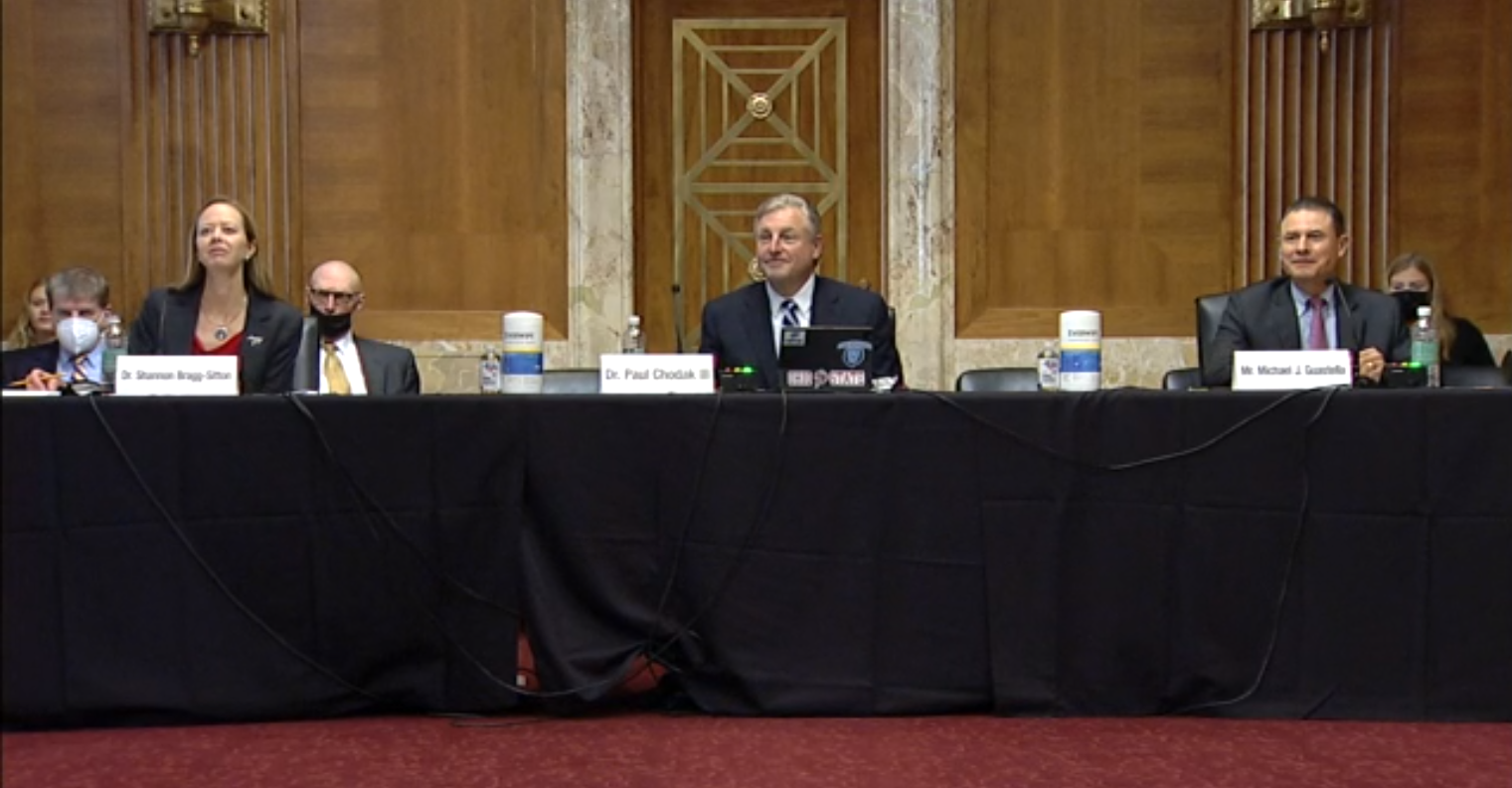
From left, Shannon Bragg-Sitton, Paul Chodak, and Michael J. Guastella appear before the Senate Committee on Energy and Natural Resources on November 4.
As Congress awaited key votes yesterday on spending bills that include production tax credits for at-risk plants and a new amendment adding $500 million in supplemental funding over five years to increase the availability of high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU), the U.S. Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee held a Full Committee Hearing On Potential Non-Electric Applications Of Civilian Nuclear Energy. Sen. Joe Manchin (D., W.V.), chairman of the committee, emphasized that “advanced nuclear reactors hold enormous potential to provide opportunity to communities across the country with zero-emission baseload power” and made it clear he expects new reactors to replace retiring coal plants in his home state of West Virginia.
Speaking before the committee were Shannon Bragg-Sitton of Idaho National Laboratory, Paul Chodak III of American Electric Power, and Michael J. Guastella of the Council of Radionuclides and Radiopharmaceuticals.